이진 검색 트리는 Search,Minimum,Maximum,Preecessor,Successor,Inserrt,Delete 를 비롯해 다양한 동적 집한 연산을 지원한다. 따라서 검색 트리를 딕셔너리 및 우선순위 큐 등 다양한 자료구조에 활용 할 수 있다.
이진 검색 트리의 기본 연산들은 트리의 높이에 비례하는 시간에 수행된다. 이로 인해 이진 검색 트리의 높이를 균일하게 유지하는 것이 중요하기에 어떤 경우에도 빠른 실행속도를 보장하기 위한 다양한 변형점들을 알아나갈 것이다.
그 전 가장 기본이 될 이진 검색 트리에 대해 먼저 알아보자
이진 검색 트리의 정의
interface BSTreeNode<T> {
key: T;
left: NullableNode<T>;
right: NullableNode<T>;
parent: NullableNode<T>;
}
type NullableNode<T> = BSTreeNode<T> | null;이진 검색 트리란 트리라는 정의에 맞게 노드를 객체로 하는 연결 자료로 표현된다. 이진 검색 트리에서 키들은 항상 다음과 같은 특성을 만족해야 한다.
"x를 이진 검색 트리의 한 노드라고 하고 y를 x의 왼쪽 서브트리의 한 노드, z를 x의 왼쪽 서브트리의 한 노드라고 하자. 이 때 y.key 는 x.key보다 항상 작거나 같아야 하며 z.key 는 x.key보다 항상 크거나 같아야 한다."
이진 트리의 삽입 (Insert)
이진 트리의 정의에 맞춰 기본 연산중 하나인 삽입 메소드를 정의해보자
const insert = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>, key: T): BSTreeNode<T> => {
const newNode: BSTreeNode<T> = { key, left: null, right: null, parent: null };
let current: NullableNode<T> = node;
let lastVisited = current;
while (current !== null) {
lastVisited = current;
current = key < current.key ? current.left : current.right;
}
if (!lastVisited) {
return newNode;
}
if (key < lastVisited.key) {
lastVisited.left = newNode;
} else {
lastVisited.right = newNode;
}
newNode.parent = lastVisited;
return node;
};이진 트리의 삽입은 이진 트리 특성에 맞춰 삽입 되기 적절한 위치의 노드를 찾고 특성에 맞춰 노드에 삽입해주면된다.
이진 트리의 순회
이진 검색 트리를 중위 순회 (inorder tree walk) 하게 되면 트리의 모든 노드들을 키 순으로 정렬된 값으로 순회 할 수 있게 된다.
note중위 순회는
Left Subtree - Node - Right Subtree순으로 순회한다.
const inorder = <T>(node: NullableNode<T>): void => {
if (node === null) {
return;
}
inorder(node.left);
console.log(node.key);
inorder(node.right);
};이진 트리의 조회
이진 트리의 특성에 맞춰 값을 조회하는 것도 매우 간단하게 구현 할 수 있다.
특정 키 값을 가진 노드 조회하기
const search = <T>(node: NullableNode<T>, key: T) => {
let current = node;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.key === key) {
return current;
}
current = key < current.key ? current.left : current.right;
}
return null;
};트리의 최소, 최대값 찾기
이진 트리의 특정 노드의 서브트리들에서 최소값이나 최대값을 찾는 연산은 대칭적으로 이뤄진다.
const findMin = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
let current = node;
while (current.left !== null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
};
const findMax = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
let current = node;
while (current.right !== null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
};두 메소드는 각자의 서브트리에서 좌측 혹은 우측 서브트리가 없을 때 까지 반복하여 순회하면 된다.
특정 노드보다 이전값이나 다음 값 찾기
이진 검색 트리의 한 노드가 주어졌을 때, 중위 트리 순회에 의해 결정되는 정렬 순서에 의한 그 노드의 직후 원소를 찾는 것이 필요 할 때가 있다. (혹은 직전)
const findSuccessor = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
if (node.right) {
return findMin(node.right);
}
let child = node;
let parent = node.parent;
while (parent !== null && parent.right === child) {
child = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
};
const findPredecessor = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
if (node.left) {
return findMax(node.left);
}
let child = node;
let parent = child.parent;
while (parent !== null && parent.left === child) {
child = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
};두 메소드는 중위순회 시 호출되는 해당 노드 이전의 노드나 이후의 노드를 찾는 메소드들이다.
중위순회는 어떤 노드 X 가 있을 때 X의 좌측 서브트리를 우선적으로 순회 한 후 본인을 순회, 이후 우측 서브트리를 순회하는 방식이다.
그러니 본인 호출 된 다음 순서를 찾는 findSuccessor 의 경우엔 우측 서브트리가 있는 경우엔 우측 서브트리의 가장 좌측 leaf node 를 찾거나, 우측 서브트리가 없는 경우엔 자신의 부모 노드 중 아직 호출되지 않은 노드를 찾아 반환한다.
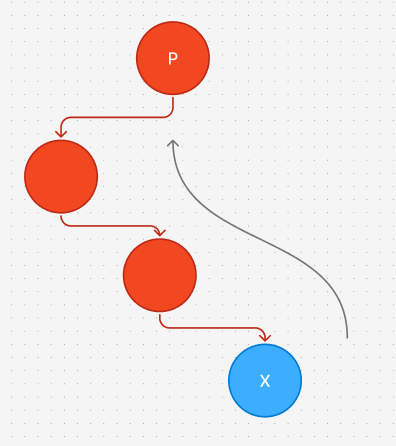 findSuccessor의 부모를 찾는 반복문의 이미지
findSuccessor의 부모를 찾는 반복문의 이미지
findSuccessor 의 while 문에서 parent.right === child 가 아닌 노드에서 멈추는 이유는 위 이미지 처럼 중위순회 시 parent.right === child 인 노드는 가장 leaf에서 이미 호출된 노드 X 가 호출되기 전에 이미 호출되었기 때문이다.
findPredecesor 도 같은 방식이다.
note사실 난 이 부분이 직관적으로 잘 이해가 안됐어서 하루동안 계속 고민했었다.
이진 검색 트리의 삭제
트리의 삽입 및 조회는 단순했지만 삭제의 경우에는 조금 복잡하다. 다양한 케이스가 있는데 그 중 한 케이스가 좀 복잡하기 때문이다.
삭제하고자 하는 노드의 자식 노드가 하나 밖에 없는 경우
삭제하고자 하는 노드 X 가 있을 때 이진 트리 특성에 따라 X 가 X.parent 의 left , right 건 상관없이 X.left, X.right 모두 X 가 만족하던 특성을 만족한다.
이에 삭제하고자 하는 노드의 자식 노드가 하나 밖에 없는 경우엔 해당 노드의 자식노드와 부모노드를 연결해주면 된다.
삭제하고자 하는 노드의 자식 노드가 두 개 모두 있는 경우
삭제하고자 하는 노드 X 의 좌측,우측 자식 노드를 L,R 이라 할 때 삭제 연산에 사용 할 서브트리를 좌측으로 하느냐 우측으로 하느냐에 따라 코드가 다르다. (대칭적이다.)
이 경우에선 우측 자식 노드를 사용하도록 한다.
모든 연산의 시작은 R 노드의 최소값, 즉 좌측 노드를 더 이상 가지지 않는 우측 서브트리의 leaf node 를 찾는다.
이 때 구해진 노드를 R.minimum 이라 해보자
R.minimum 은 R 노드이거나 (R 노드가 우측 서브트리만 가진 기울어진 트리인 경우) 그렇지 않은 경우로 나뉜다.
R.minimum 이 R 노드인 경우
이경우는 단순하게 X 노드의 부모노드와 좌측 서브트리를 R 노드에 연결해주면 된다.
R.minimum 이 R 노드가 아닌 경우
이 경우엔 두 번의 연결들이 필요하다.
우선 R.minimum 의 우측 서브트리와 R.minimum 의 부모 노드를 연결해준다. 즉 R.minimum 노드가 있던 자리는 R.minimum.right 노드가 대체한다.
이후 X 노드의 부모노드와 좌측 서브트리를 R 노드에 연결해준다.
const deleteNode = <T>(root: NullableNode<T>, key: T): NullableNode<T> => {
const targetNode = search(root, key);
if (!targetNode) {
return root;
}
const transplant = (
nodeToReplace: BSTreeNode<T>,
replacementNode: NullableNode<T>
) => {
const parentNode = nodeToReplace.parent;
if (!parentNode) {
root = replacementNode;
} else if (parentNode.left === nodeToReplace) {
parentNode.left = replacementNode;
} else {
parentNode.right = replacementNode;
}
if (replacementNode) {
replacementNode.parent = parentNode;
}
};
if (!targetNode.left) {
transplant(targetNode, targetNode.right);
return root;
}
if (!targetNode.right) {
transplant(targetNode, targetNode.left);
return root;
}
const successor = findMin(targetNode.right);
if (successor.parent !== targetNode) {
transplant(successor, successor.right);
successor.right = targetNode.right;
targetNode.right.parent = successor;
}
transplant(targetNode, successor);
successor.left = targetNode.left;
targetNode.left.parent = successor;
return root;
};전체 코드
interface BSTreeNode<T> {
key: T;
left: NullableNode<T>;
right: NullableNode<T>;
parent: NullableNode<T>;
}
type NullableNode<T> = BSTreeNode<T> | null;
const insert = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>, key: T): BSTreeNode<T> => {
const newNode: BSTreeNode<T> = { key, left: null, right: null, parent: null };
let current: NullableNode<T> = node;
let lastVisited = current;
while (current !== null) {
lastVisited = current;
current = key < current.key ? current.left : current.right;
}
if (!lastVisited) {
return newNode;
}
if (key < lastVisited.key) {
lastVisited.left = newNode;
} else {
lastVisited.right = newNode;
}
newNode.parent = lastVisited;
return node;
};
const inorder = <T>(node: NullableNode<T>): void => {
if (node === null) {
return;
}
inorder(node.left);
console.log(node.key);
inorder(node.right);
};
const search = <T>(node: NullableNode<T>, key: T) => {
let current = node;
while (current !== null) {
if (current.key === key) {
return current;
}
current = key < current.key ? current.left : current.right;
}
return null;
};
const findMin = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
let current = node;
while (current.left !== null) {
current = current.left;
}
return current;
};
const findMax = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
let current = node;
while (current.right !== null) {
current = current.right;
}
return current;
};
const findSuccessor = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
if (node.right) {
return findMin(node.right);
}
let child = node;
let parent = node.parent;
while (parent !== null && parent.right === child) {
child = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
};
const findPredecessor = <T>(node: BSTreeNode<T>) => {
if (node.left) {
return findMax(node.left);
}
let child = node;
let parent = child.parent;
while (parent !== null && parent.left === child) {
child = parent;
parent = parent.parent;
}
return parent;
};
const deleteNode = <T>(root: NullableNode<T>, key: T): NullableNode<T> => {
const targetNode = search(root, key);
if (!targetNode) {
return root;
}
const transplant = (
nodeToReplace: BSTreeNode<T>,
replacementNode: NullableNode<T>
) => {
const parentNode = nodeToReplace.parent;
if (!parentNode) {
root = replacementNode;
} else if (parentNode.left === nodeToReplace) {
parentNode.left = replacementNode;
} else {
parentNode.right = replacementNode;
}
if (replacementNode) {
replacementNode.parent = parentNode;
}
};
if (!targetNode.left) {
transplant(targetNode, targetNode.right);
return root;
}
if (!targetNode.right) {
transplant(targetNode, targetNode.left);
return root;
}
const successor = findMin(targetNode.right);
if (successor.parent !== targetNode) {
transplant(successor, successor.right);
successor.right = targetNode.right;
targetNode.right.parent = successor;
}
transplant(targetNode, successor);
successor.left = targetNode.left;
targetNode.left.parent = successor;
return root;
};